Course Schedule
- Week 1: Intro to GAI Tools
- Week 2: Solve General Problems with GAI Tools
- Week 3: Use GAI Tools as Effective Study Aid
- Week 4: Apply GAI Tools to Advanced Learning Use Cases (I) - Computing Domains
- Week 5: Apply GAI Tools to Advanced Learning Uses Cases (II) - Non-Computing Domains
- Week 6: Adverse Use and Societal Implications of GAI Tools
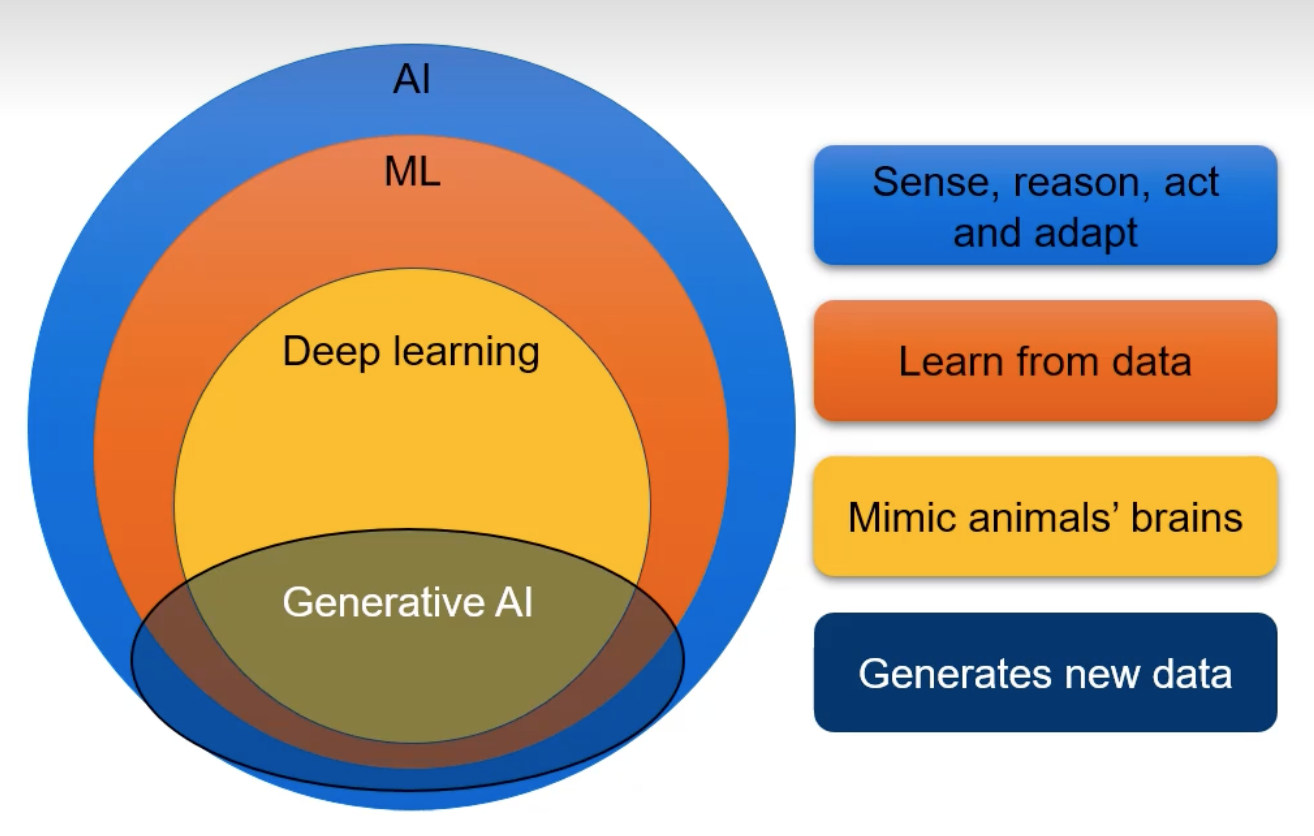
What is AI?
A branch of computer science devoted to developing data processing systems that perform functions normally associated with human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, and self-improvement.
Quote
The science and engineering of making intelligent machines
- John McCarthy
What is ML?
Learns the pattern through large amounts of data and make a decision on previously unseen data.
What is Generative AI?
System that can generate new data!! Built on complex neural network
Applications:
- Text Generation
- Image Generation
- Audio Generation
- Video Generation
Natural Language Processing
Subfield of AI that focuses n enabling computers to understand, interpret, generate, and manipulate language. The language model! e.g. Speech - to - text models! Translation! Information retrieval!
Underlying Concepts in NLP
- Tokenisation: breaking down text into individual-tokens
- N-grams: Continuous sequence of n-items
- e.g. bigrams [“Singapore is”, “is beautiful”]
- Helps to capture context but may fail to capture global context
- Embeddings: Numerical representation of words or sentences
- common models: Word2Vec, GloVe
n-gram Probabilistic Model - Language Generation
Simple approach to language model. Estimate the probability of the nth words based on the previous (n-1) words.
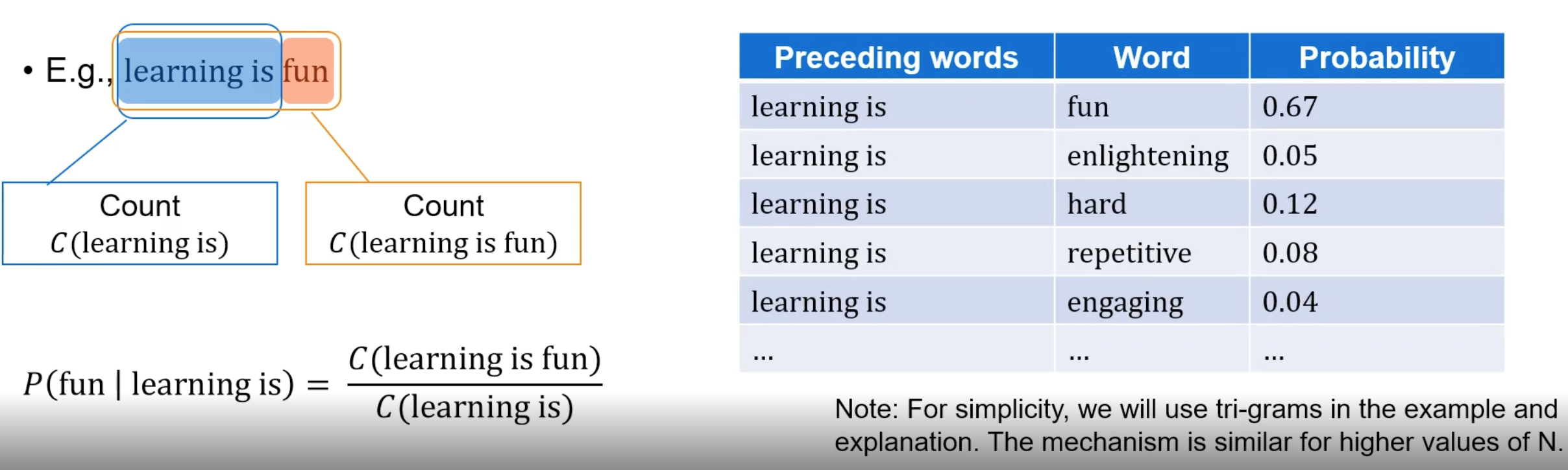 Key Considerations:
Key Considerations:
- Unseen n-grams (words that were not seen during training)
- smoothing
- Data sparsity: some n-grams may not be seen during training
- Limited context will affect accuracy
Neural Network Based Models
Train neural network to predict next word in the sequence ?? Recognize patterns and relationships between words.
e.g. Recurrent neural networks (RNN)
- Maintains an internal state that summarises the history of previous inputs
- capture temporal dependencies
- retain context from earlier elements in the sequence
- Limitations:
- Vanishing gradient problem
- Sequential → computationally expensive; impacts scalability
- Improvements on RNN:
- Long Short-Term Memory and Gated Recurrent Unit networks
Transformers and Large Language Models
Encoder-Decoder Networks
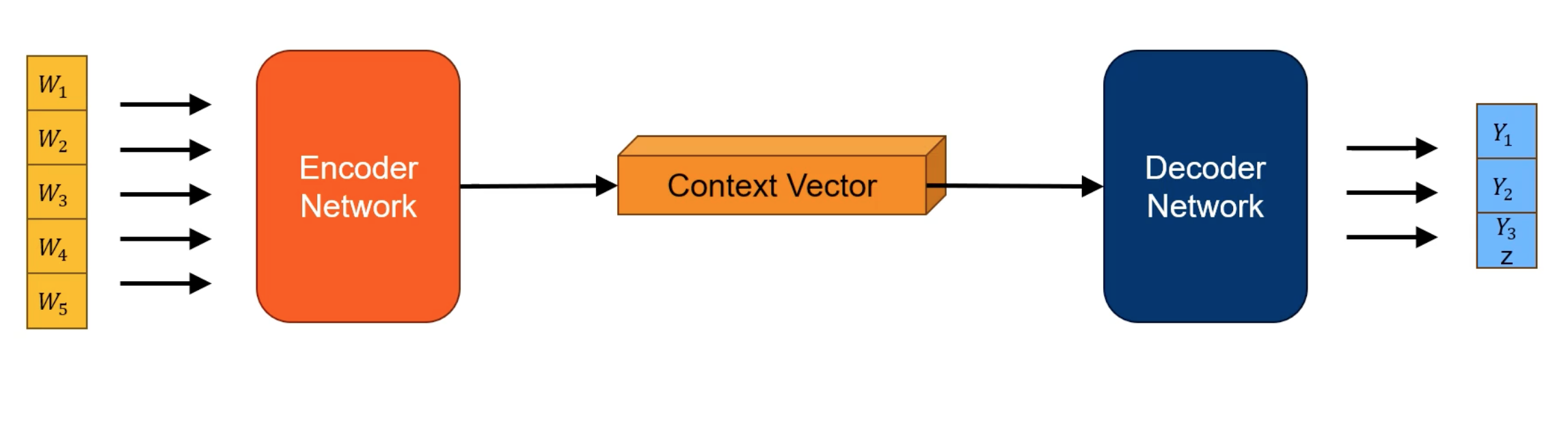 Decoder network will generate the output one word at a time.
e.g. translation, text summarization
Decoder network will generate the output one word at a time.
e.g. translation, text summarization
Encoder only: classification, sentiment analysis Decoder only: Text completion & Generation, image captioning
Limitations:
- inefficient in dealing with long input sequences
- Loss of information
Workarounds: The Attention Mechanism!
- Gives the encoded network a hidden state which has some sort of attention score
- Context vector has a weighted sum which gives the decoder state an idea of which context is more important
Advantages (compared to Long Short-Term Memory and Gated Recurrent Unit Networks):
- Efficiency
- Interpretability
- Global context
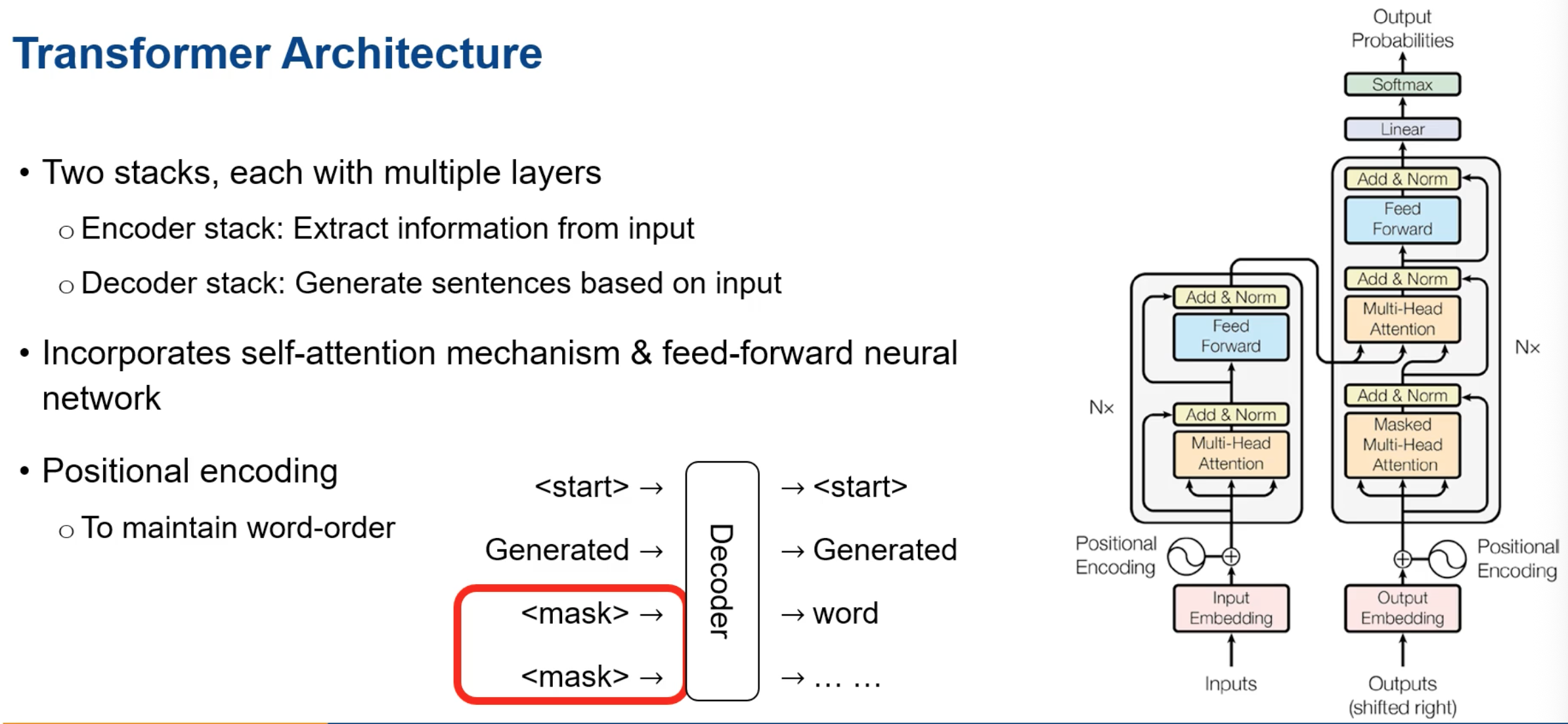
Transformer Architecture
Reinforcement Learning:
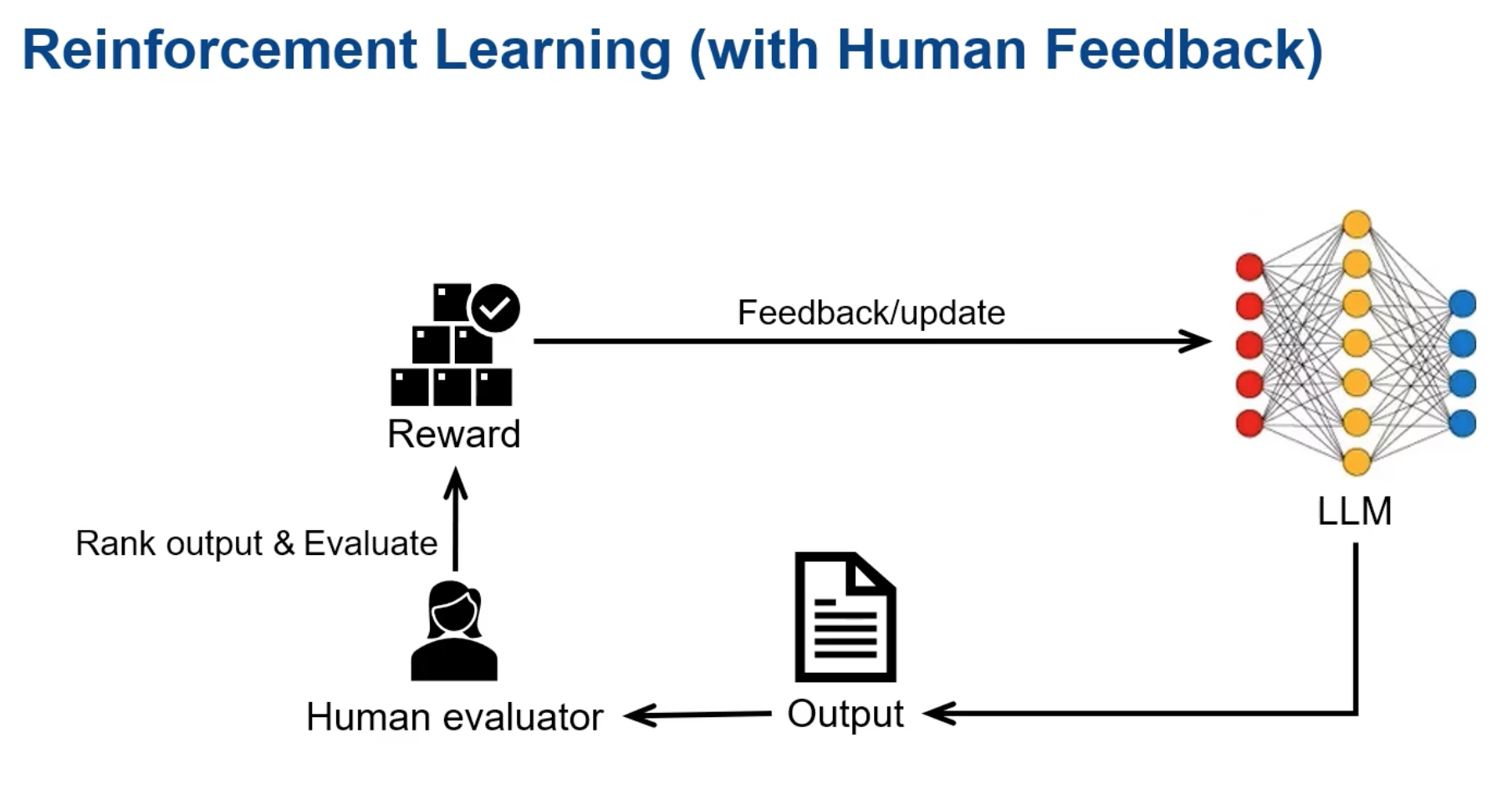
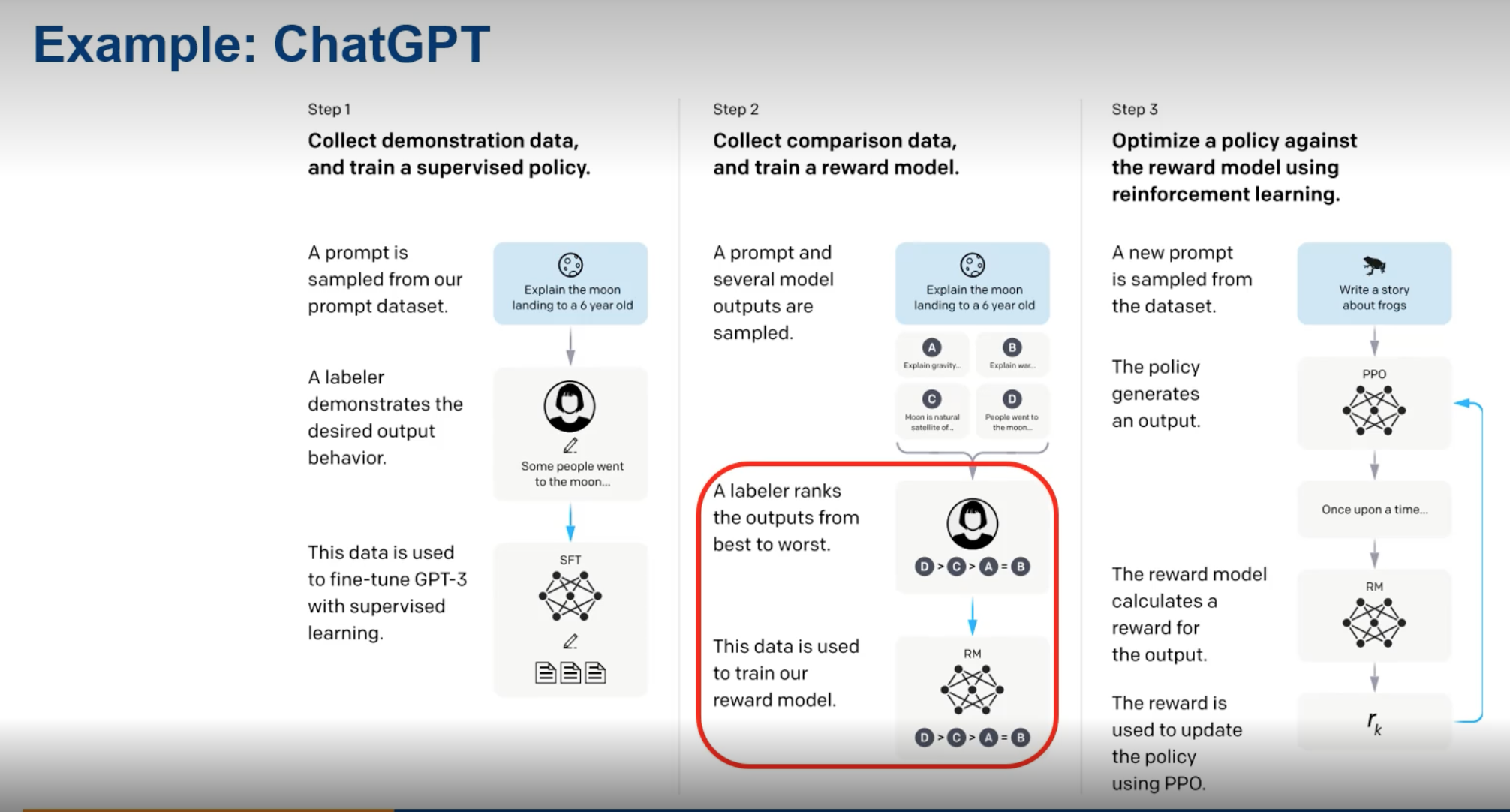
Reinforcement Learning Example: ChatGPT
Learning objectives
- GAI tools are expected to disrupt the ways students learn, presenting objectives as well as challenges.
- AI would impact 60% of advanced economy jobs!! How to adapt?
- Learn how to simulate critical thinking and problem solving skills with the help of AI.
Reflections
- Wow it seems that this course is planned with the help of ChatGPT !?