TODO
- Download PostgreSQL
- Try following the examples in the lecture, learn how to set up PostgreSQL
Case Study: Game
You want to store the following data:
Customer:
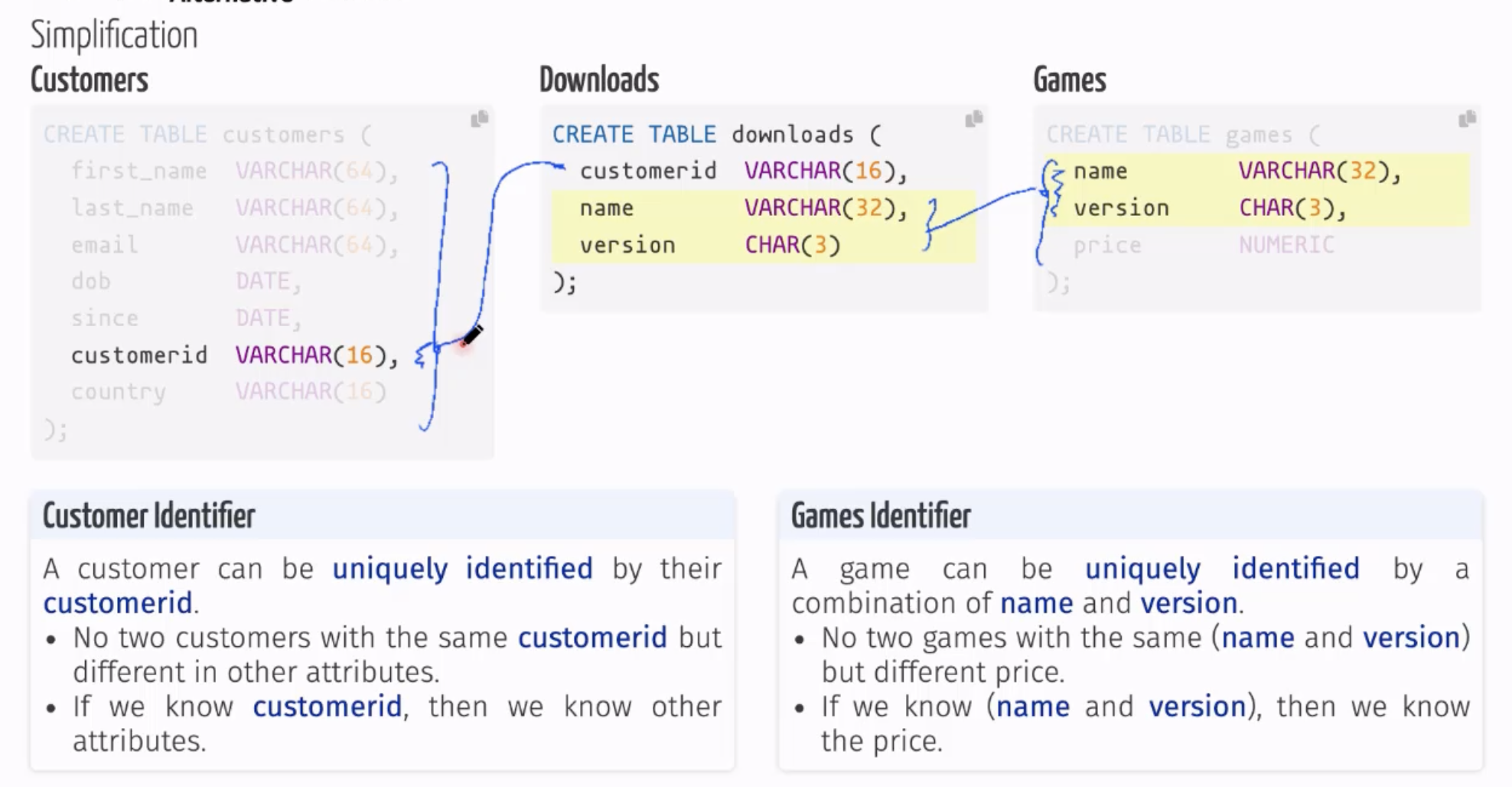
- first name, last name, dob, email, regs, id Games:
- name, version, price Downloads:
- customer, game
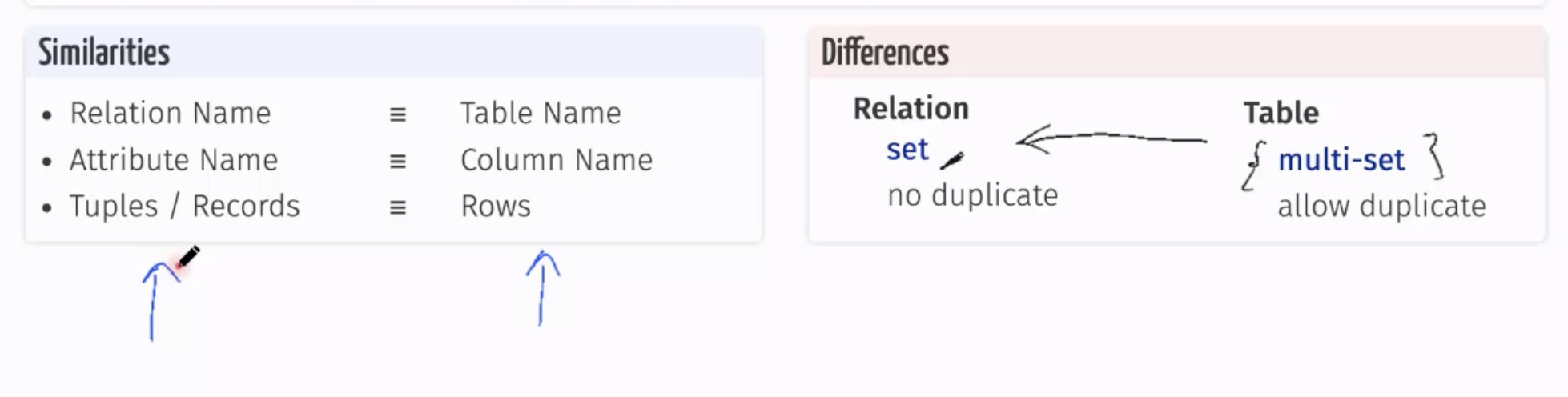
Relational Model
The relational model proposes to organise data in relations, Relations have a name and attributes. Attributes have a name.
 The above is called a relation because the table relates the customer data to a game data to form an information of “which customer download which game”.
The above is called a relation because the table relates the customer data to a game data to form an information of “which customer download which game”.
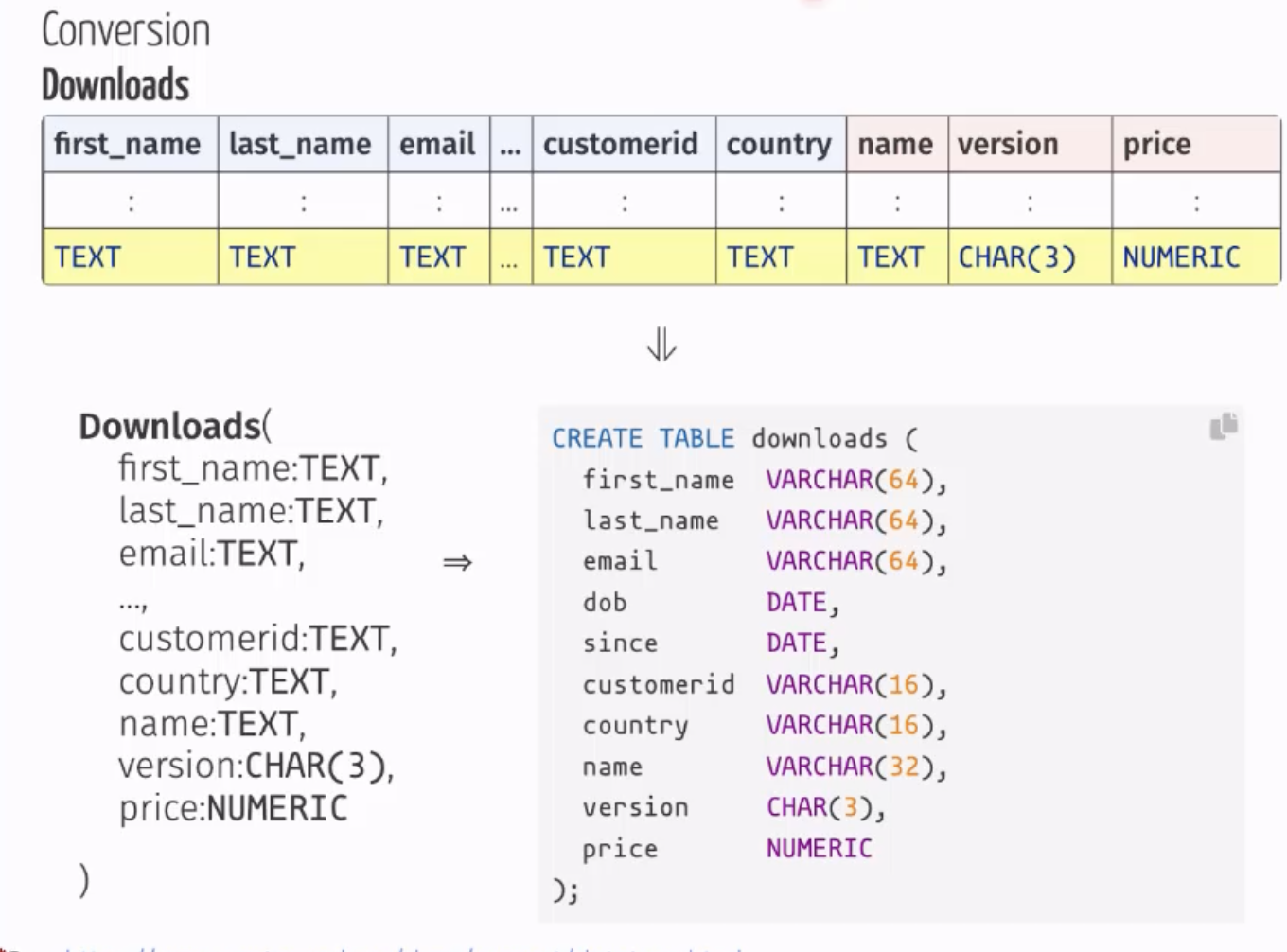
Data Types
- TEXT
- CHAR (e.g. CHAR(3) for 1.0)
- NUMERIC
Questions
- What is DBMS?
What I’ve learnt/ been exposed to
- Client Architecture
- Three-Tier Architecture
- Steps to use SQL
- Design the structure of the table
- Summarize the table as relational schema
- Separate attributes into comma separated lines
- Translate into SQL CREATE TABLE statement
Integrity Constraints
- You can define contraints for your database and you want to ensure that your database always complies to the constraints
When you make a commit there can be two outcomes
- Deferrable constraints are inconsistent
- you rollback to the last consistent state.
- Constraints are consistent
- The changes you make are committed
- The changes are permanent
SQL Support five kinds of integrity constraints
PRIMARY KEY: Unique combination of values and cannot be NULLNOT NULLUNIQUEFOREIGN KEY: Value exist in referenced table or value contains NULLCHECK: Arbitrary Boolean expression check ??
Definitions
Info
Relational Schema: the summary of the structure of the table. It contains the name of the relation as well as the name, order, and domain of the attributes
Set of Tuples: no duplicate in a set, unordered. Tuple is however ordered.