What is AI ?
“Study of agents that receive percepts from the environment and perform actions”
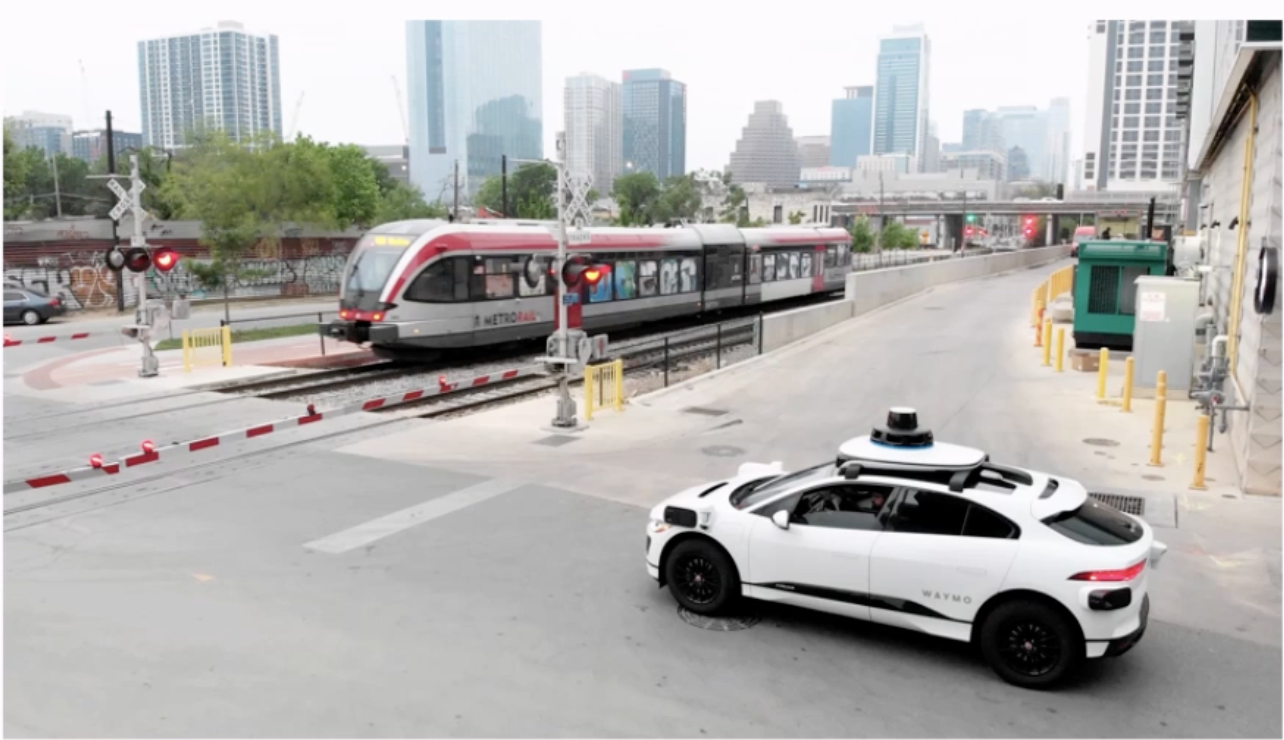 In the picture above, the car is an agent that has a few goals to achieve (e.g. reach a destination, save fuel, keep passenger safe). From these goals, you want to measure the performance of the car. A rational agent will then choose actions that maximize performance measure
In the picture above, the car is an agent that has a few goals to achieve (e.g. reach a destination, save fuel, keep passenger safe). From these goals, you want to measure the performance of the car. A rational agent will then choose actions that maximize performance measure
PEAS Framework
Performance Measure, Environment, Actuators , Sensors
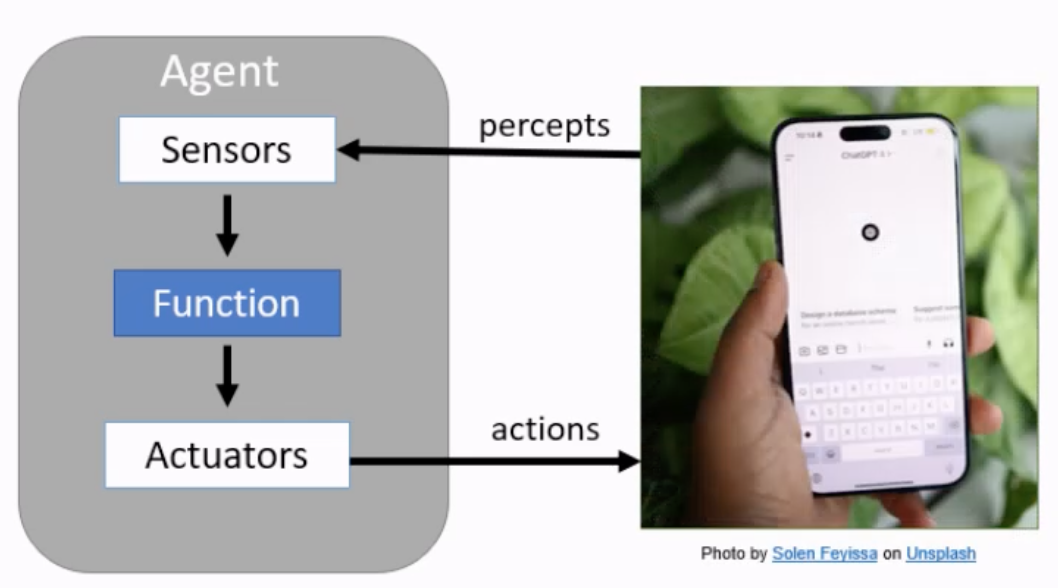
Agent Function
Maps from percept histories to actions
An agent is completely specified by the agent function.
Properties of the Environment
- Fully observable/ Partially observable
- e.g. chess board vs self-driving car
- Single/ multi-agent
- e.g. chess (player v player) multi-agent
- e.g. cat classifier
- Deterministic vs stochastic
- The next state of environment is completely determined by the current state and the action executed by the agent
- If the environment is also dependent on the actions of other agents, then it is also strategic. However, if the other agents are predictable (their strategies are fixed and only dependent on the state, then the other agents can be subsumed as parts of the environment)
- e.g. chess is deterministic + strategic, self driving car is stochastic because the next state of environment is not very predictable ?
- Episodic (vs sequential)
- The agent’s experience is divided into atomic “episodes”
- The choice of action in each episode depends only on the episode itself
- episodic: image classification
- sequential: chess
- Static (vs dynamic)
- environment is unchanged
- can be semi-dynamic if the environment itself does not change within the passage of time, but the agent’s performance score. E.g. (chess timed, within the same passage of time, the agent’s performance score changes)
- Discrete (vs continuous)
- Limited number of distinct, clearly defined percepts and actions.
Simple Reflex Agent
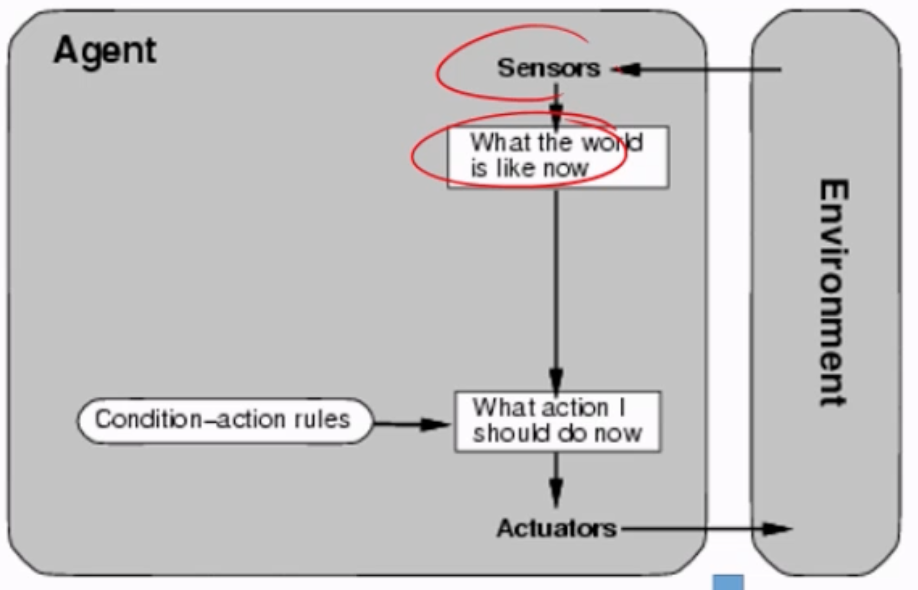 You are able to decide what actions you should do based on simple if-else statements
You are able to decide what actions you should do based on simple if-else statements
Goal-based Agent
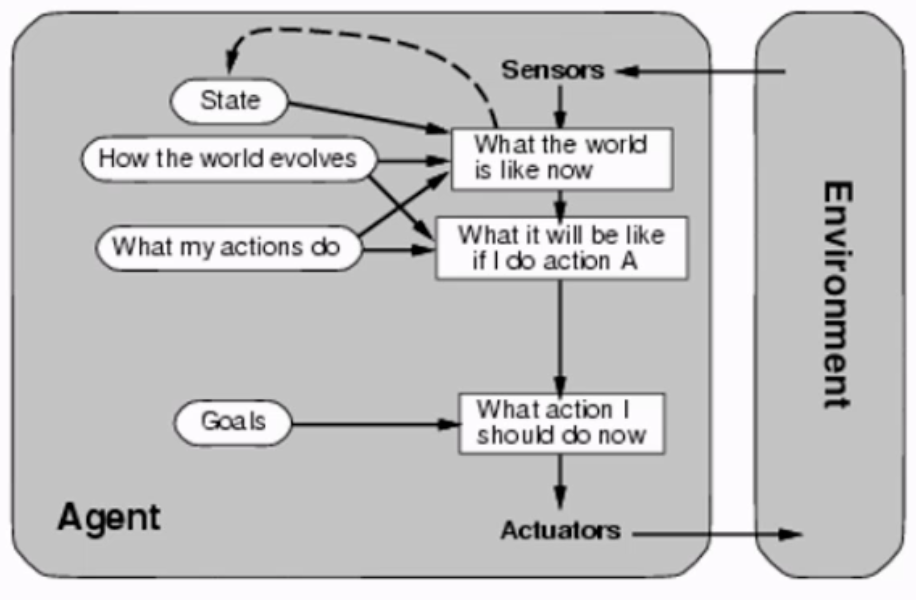 Agent will reason about the world, and do action based on the goals.
Agent will reason about the world, and do action based on the goals.
Utility-based Agent
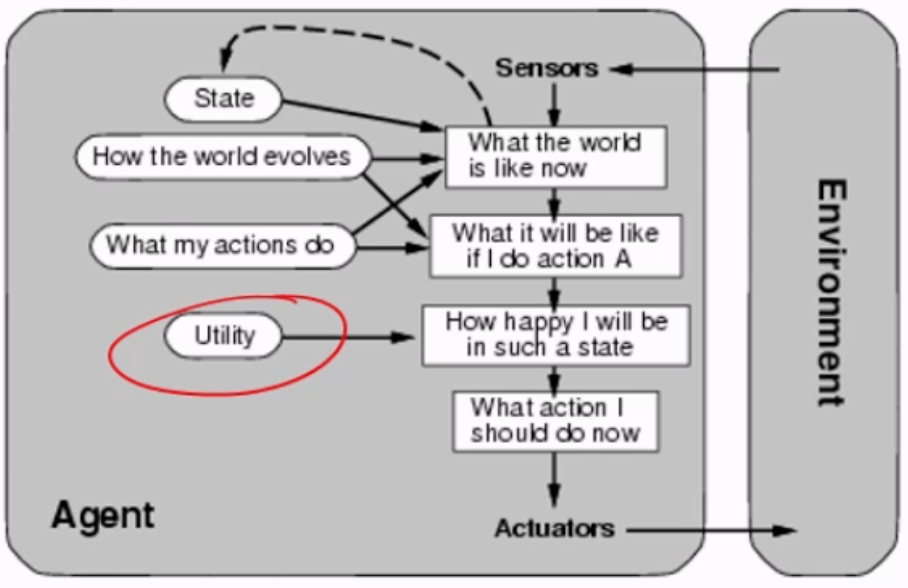 Adds an additional step to the goal-based agent, and from there decides what action to do.
Adds an additional step to the goal-based agent, and from there decides what action to do.
Learning Agent
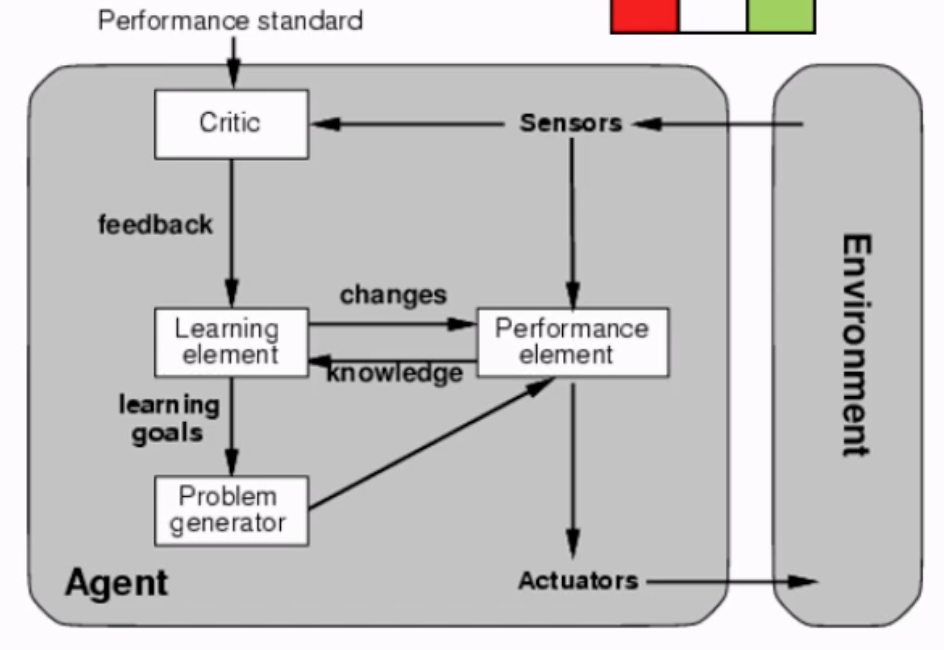 Designed to improve its performance over time by using experience. it does so by adjusting how it selects actions so that it performs better with respect to a given performance in its environment. (Will not be taught in CS2109s)
Designed to improve its performance over time by using experience. it does so by adjusting how it selects actions so that it performs better with respect to a given performance in its environment. (Will not be taught in CS2109s)
Designing an Agent
Trying to design an agent for problems that can be solved by searching (e.g. path finding).
Environment: map Properties: Fully-observable, deterministic (our action leads to a deterministic result), static, discrete
- From the properties, we only have to look at the map nce.
Requirements for the agent:
- a goal, or a set of goals
- A model of the environment
- A search algorithm